Unlock a world of possibilities! Login now and discover the exclusive benefits awaiting you.
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
One basic way to assign a value to a variable is to use a Let statement in the script:
Let vToday = Num(Today()) ;
This will calculate the expression and assign it to the variable when the script is run. This is exactly what you want if you want to use a variable as a numeric parameter in your expressions.

But if you want the expression to be evaluated at a later stage, e.g. every time the user clicks, what should you do then? One way is to store the expression as a string in the variable, using either the Set or the Let statement or by defining it in the Document Properties -> Variables:
Set vSales = Sum(Sales) ;
Let vSales = 'Sum(Sales)' ;
In neither case, the expression will be calculated. The variable will contain the string ‘Sum(Sales)’, which subsequently can be used in an expression using a dollar expansion: $(vSales).
With a dollar expansion, QlikView will substitute the ‘$(vSales)’ with ‘Sum(Sales)’ before the expression is evaluated. Some of you will recognize this as an old style assembler macro expansion. The subsequent calculation will be made based on the evaluation of the resulting expression. Note the two steps: (1) Variable expansion; and (2) Expression evaluation.
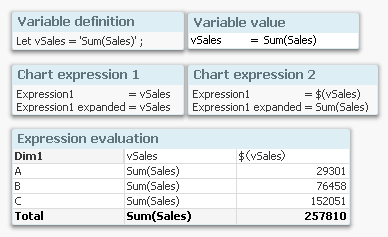
In the chart above, you can see the result of using a normal variable reference (the first expression) or using a dollar expansion (the second expression). In the second expression, the variable is expanded and the numbers are calculated correctly.
But this is just the beginning…
It is also possible to calculate the variable value, i.e. determine how it should be expanded, by using an initial equals sign in the variable definition.
Let vSales2 = '=Sum(Sales)';
In this case, the variable value is calculated after each click, whereupon the dollar expansion in the chart expression is made, and finally the expression is evaluated. This means that the evaluation of ‘Sum(Sales)’ is done before the variable expansion. Note the three steps: (1) Variable calculation; (2) Variable expansion; and (3) Expression evaluation.
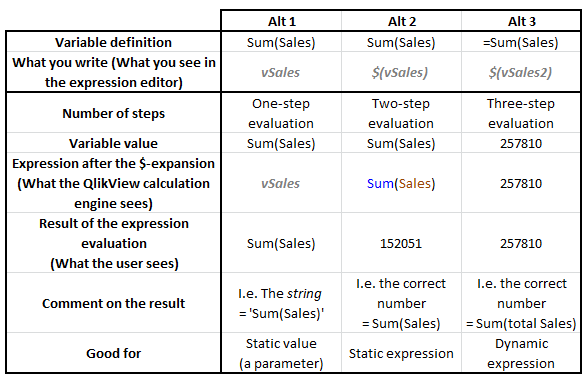
The table below summarizes the three methods.
With the above, you can do almost magical things. You can for instance make conditional calculations that depend on e.g. selections, client platform or user.
Example:
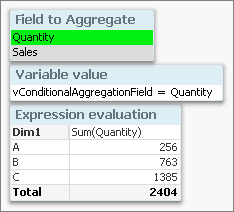
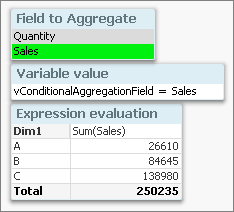
- Create a field [Field to Aggregate] containing the names of two other numeric fields: 'Quantity' and 'Sales'
- Create a variable vConditionalAggregationField = '=Only([Field to Aggregate])'
- Create a chart with an expression = Sum($(vConditionalAggregationField))
The calculation in a chart will now toggle between Sum(Quantity) and Sum(Sales) depending on your selection.
The use of variables is an extremely powerful tool that you can use to create flexible applications. Use it – but with caution. Too much magic behind the curtains can be confusing.
Further reading related to this topic:
- « Previous
- Next »
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.