Unlock a world of possibilities! Login now and discover the exclusive benefits awaiting you.
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
A master calendar table is a dimensional table that links to a date in the data, e.g. OrderDate. The table usually does not exist in the database, but is nevertheless needed in the QlikView application for a proper analysis. In the master calendar table you can create all time and date fields that you think the user needs; e.g. Month, Year, Quarter, RollingMonth, FiscalMonth or flags like IsCurrentYear, etc.
A typical master calendar tables contains one record per date for the time period used in the QlikView app, perhaps a two-year period, i.e. 730 records. It is in other words a very small (short) table. Since it is small, you can allow yourself to have many fields in it – it will not affect performance in any significant way.
There are in principle three ways you can generate the records (with an infinite number of variations in the details):
- Load from the fact table, e.g.
Load distinct Date, Month(Date) as Month … resident TransactionTable ; - Generate all dates within a range, using autogenerate, e.g.
Load Date, Month(Date) as Month … ;
Load Date($(vStart) + RecNo()) as Date autogenerate $(vEnd) - $(vStart) ; - Generate all dates within a range, using a while loop, e.g.
Load Date, Month(Date) as Month … ;
Load Date(MinDate+iterno()) as Date While iterno() <= MaxDate - MinDate ;
Load Min(Date)-1 as MinDate, Max(Date) as MaxDate resident TransactionTable
In the first case you use the table to which you are going to link the master calendar. This way you will get exactly those values that really exist in the database. Meaning that you will also miss some dates – e.g. Saturdays and Sundays most likely - since they often do not exist in the database.
In the second case, you generate a range of dates. This is a good solution, but it means that you will need to define the range beforehand. There are several ways to do this, e.g. find largest and smallest value in the data; or hard-code the days for the relevant year.
In the third solution, you generate all dates between the first and last date of your transaction table. This is my preferred solution. Optionally you can use YearStart(Min(Date)) and YearEnd(Max(Date)) to define the range.
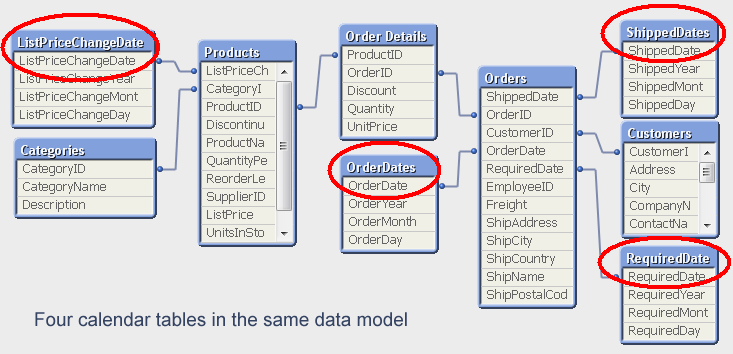
The word "Master" for the calendar table is really misleading. There is no reason to have only one calendar table. If you have several dates, you should in my opinion use several calendar tables in the same data model. The alternative - to have the same calendar for all dates - is possible using a link table but complicates the data model and limits how the user can make selections. For example, the user will not be able to select OrderMonth=’Sep’ and at the same time ShipperMonth=’Nov’.
Bottom line: Use a calendar table whenever you have a date in your database. Use several if you have several dates.
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.