Unlock a world of possibilities! Login now and discover the exclusive benefits awaiting you.
- Qlik Community
- :
- Support
- :
- Support
- :
- Knowledge
- :
- Support Articles
- :
- Low-code Automation for Google BigQuery
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Low-code Automation for Google BigQuery
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Low-code Automation for Google BigQuery
Jan 20, 2022 10:58:46 AM
Nov 23, 2020 5:35:10 PM
Abstract
Google BigQuery is a market leading cloud data warehouse that provides exceptional performance when manipulating large data sets for analytic workloads. However, although it offers virtually hands-free management, there are many good reasons why you should complement BigQuery with low-code automation solutions to improve productivity. This article explains how you can improve your operational efficiency in just six steps with Qlik’s Data Warehouse Automation Solution for Google BigQuery.
Google BigQuery Overview
Google BigQuery is a cost-effective, highly scalable, serverless data warehouse designed for business agility. The platform manages all resources, scales automatically and is highly available. Consequently warehouse administrators don’t have to spend time making typical implementation decisions like CPU sizing or maximum storage allocation.
Google BigQuery is a columnar data warehouse that stores data in column structures rather than rows used by traditional databases. As a result, it’s lighting fast for aggregation type queries, but this also means it works best with demoralized data whenever possible. Denormalization increases query performance of large data sets by localizing the necessary data to individual nodes and reduces the shuffling of data between them.
Google BigQuery also supports two different SQL dialects:
- Standard SQL: Standard SQL is compliant with the SQL 2011 standard and is the preferred dialect for querying data.
- Legacy SQL: This dialect was supported by the first version of BigQuery; however it does not support querying nested and repeated data.
For a complete explanation of the Google BigQuery Architecture click on the following link:
https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/data-analytics/new-blog-series-bigquery-explained-overview
Why Automate Google BigQuery With Qlik?
You might think that since Google BigQuery has removed much of the manual drudgery associated with data warehouse administration, then there’d be little need to increase productivity. However, there’s plenty of room for improvement, such as:
- Improve Initial data loading
- Reducing manual SQL coding warehouse administration
- Automating data warehouse updates
- Decreasing the time required to prep and provision data for downstream analytics
In fact, we can automate these areas and many more with the Qlik Data Integration (QDI) platform. The latest release of the QDI solution is optimized for Google BigQuery and automates many aspects of BigQuery operation. For example, we can use Qlik Replicate for near real-time change data capture and Qlik Compose for Data Warehouses to build internal data warehouse structures and provision data mart datasets. In addition, Qlik Compose for Data Warehouses also automates workflows that incrementally load or fully rebuild transactional data mart tables. Furthermore, the data warehouse and data mart ETL scripts generated by Qlik are pushed down to BigQuery for execution. Finally the Qlik generated workflows can be scheduled to load source data changes both to the data warehouse and to data mart tables too.
Qlik Data Integration for Google BigQuery
The following paragraphs describe features specifically created and optimized for data warehouse automation. They are as follows:
- Data Warehouse Model Generation
- Automated Mapping Generation
- Data Warehouse ETL Generation
- Data Mart ETL Generation
- Workflow Generation and Orchestration
Datawarehouse Model Generation
Qlik Compose for Data Warehouses makes it easy to generate a logical model from source data by connecting to source and introspecting the metadata to produce a model that conforms to the third normal form(3NF)/Data Vault methodology. In addition, logical models can be imported from an Erwin logical or physical model. Alternatively, data entity relationship and attribute relationships can also be manually created.
Qlik also provides support for assigning Type1/Type2 history attributes within your logical models. Qlik maps the Type 1 attributes to a hub table in the physical model and Type 2 attributes to the satellite, allowing history to be stored by attribute and not by row. This optimization improves the data loading process for the BigQuery dataset tables.
Automated Mapping Generation
Qlik Compose for Data Warehouses will create the BigQuery dataset tables and generate Mappings for the full and change data capture ETL sets. In the ETL sets Compose will automatically generate table mappings between the landing area columns and staging columns for the BigQuery Datawarehouse dataset tables. Within the automated mappings expressions, validation and cleansing rules can be applied for the mappings without complex BigQuery SQL development, which will save development lifecycle time building a data warehouse on BigQuery.
Data Warehouse ETL Generation
Qlik automatically generates and orchestrates the SQL syntax required to execute the ETL process within BigQuery that complete the full load of the tables in the data warehouse. Qlik also automatically generates and orchestrates the SQL syntax necessary to load the change data capture data into BigQuery datasets. Qlik executes the generated SQL syntax through a JDBC connection with BigQuery and utilizes BigQuery compute resources.
Data Mart ETL Generation
Qlik provides a data wizard that automatically creates a transactional data mart utilizing the BigQuery data warehouse data set. Since transactional data marts uses a star schema design versus the native columnar structure of BigQuery, Qlik Compose will automatically flatten the dimensions in the Star schema. Once again Qlik’s automation refreshes data in a transactional BigQuery data mart without complex manual transformation or scripting.
Workflow Generation and Orchestration
You can also use Qlik to generate a full and change data capture workflow with tasks to load the BigQuery data warehouse and data mart tables. The workflows to load CDC data can be scheduled through Qlik or from a third-party scheduling tool. Additionally, deployment packages that contain the metadata of each BigQuery workflow can be created to support different environments. Finally, out of the box Integration with locally installed or remote source code repositories such as Git, makes workflow orchestration easy to deploy.
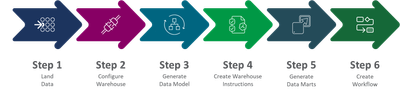
Six Steps to Google BigQuery Automation
It just takes six steps to automate Google Big Query with Qlik and they are as follows:
Step 1. Automate Data Ingest and Update
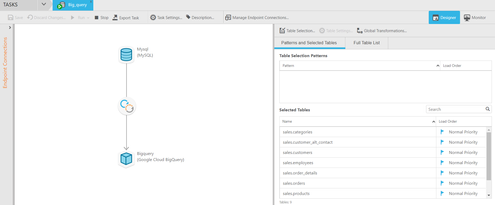
Configure Qlik Replicate Task to use Google BigQuery as an endpoint. The Google BigQuery target endpoint will utilize a Service Account Key that gives access to BigQuery. (Add required roles to Service Account for access to BigQuery.)
Qlik Replicate will create the dataset in BigQuery from virtually any data source whether on-premises or in the cloud. Once Qlik Replicate completes the full data load the tasks transitions to Change Data Capture (CDC) mode to replicate source data changes in near real-time.
Figure 1. Qlik Replicate Task for BigQuery Target
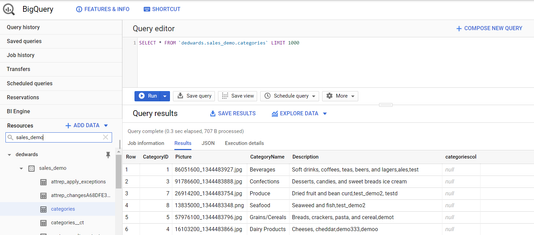
Figure 2. Google BigQuery landing dataset tables from a Qlik Replicate task
Step 2. Qlik Compose Source and Data Warehouse Configuration
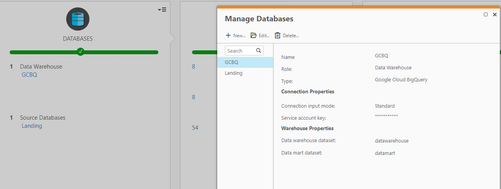
Configure a Qlik Compose for Data Warehouses project landing and data warehouse connection. The data warehouse connection will provide details of the target data warehouse and data mart dataset. The landing connections specifies the BigQuery data set that will be used for integration within the data model.
Figure 3. Qlik Compose for Data Warehouses Database Connection
Figure 4. Qlik Compose for Data Warehouses Database Landing Connection
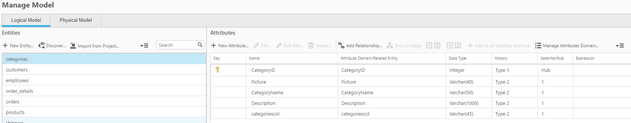
Step 3. Automatically Generate the Warehouse Data Model
The model panel is used to intelligently discovered table metadata for the logical and physical data warehouse model. Manage Model controls which attribute changes and history types can be applied to the data warehouse model.
Figure 5. Qlik Compose for Data Warehouses Manage Model
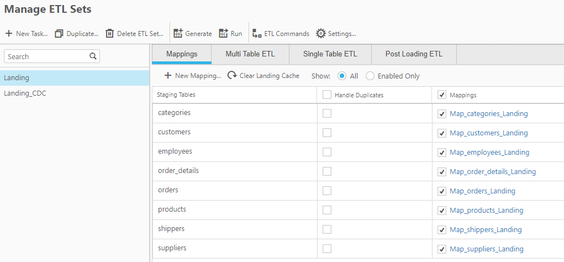
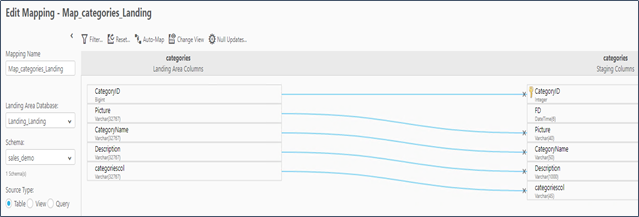
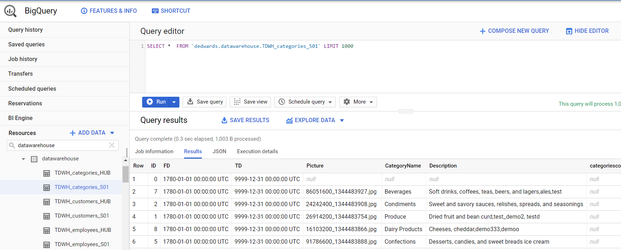
Step 4. Generate Data Warehouse Automation Instructions
The data warehouse panel selects tables that will be created as Google BigQuery tables in the data warehouse dataset. Table mappings will be created that manage the relationships between the landing and staging columns in the BigQuery tables. You can modify the mappings via expressions, lookups and data validation rules. Once completed, the ETL process code is generated and ready for execution on BigQuery. The ETL command set task (SQL syntax) can be directly initiated from within Qlik Compose.
Figure 6. Qlik Compose for Data Warehouses Full ETL Set mappings
Figure 7. Qlik Compose for Data Warehouses Mapping
Figure 8. Google BigQuery dataset tables
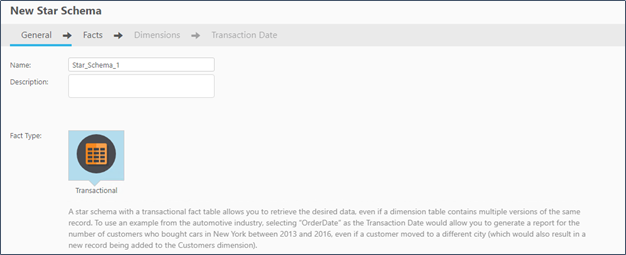
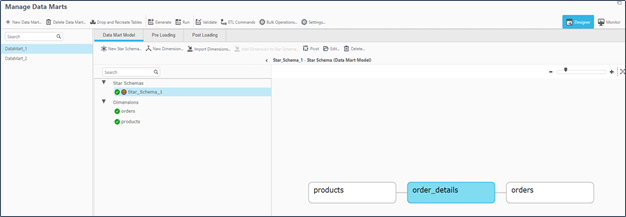
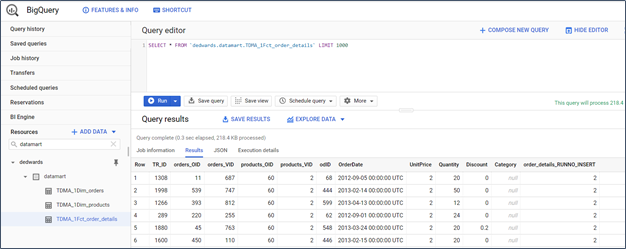
Step 5. Create Transactional Data Marts
The data mart panel provides a “New Star Schema” wizard to create the transactional star schema. The wizard starts by asking you to choose a fact table from the data warehouse dataset. You then select the parent dimension tables for the chosen fact table. You also select an attribute to serve as the transaction date for the schema. Once the schema wizard completes, BigQuery syntax is generated and executed to load create and load the data mart tables.
Figure 9. Qlik Compose for Data Warehouses data mart wizard
Figure 10. Qlik Compose for Data Warehouses data mart manager
Figure 11. Google BigQuery data mart dataset tables
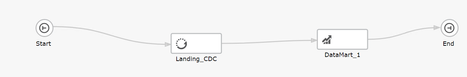
Step 6. Orchestrate the Warehouse Workflow
When the data warehouse CDC ETL set, process commands are generated a task is created and added to the default CDC workflow in the Qlik Compose monitor screen. A data mart task is also added to the default CDC workflow.
Figure 12. Orchestrating a Qlik Compose for Data Warehouses CDC workflow
Qlik and Google
Perhaps at this point you’re wondering whether third party productivity solutions are endorsed by Google. Well I’m happy to say they are. Qlik is a Google Cloud premier partner with an expertise workload designation of “SAP on Google Cloud”. The expertise designation indicates that Qlik demonstrated customer success in the described discipline. Meaning the integration of Google Cloud and Qlik helps customers extract and deliver data to Big Query for any type of downstream analysis. The joint solution helps customers see increased benefit from BigQuery with wider use of SAP data alongside other data sources across their organization.
Summary
Google BigQuery is a market leading cloud data warehouse that provides exceptional performance when manipulating large data sets for analytic workloads. Although BigQuery offers virtually hands-free management Qlik’s Data Warehouse automation solution will save you significant development time when used with the Google platform. Complete the following form to request a personalized demonstration of Qlik’s low-code data warehouse automation solution.